2024 Ehrlichia spp. Forecast
Ehrlichia spp. Forecast 2024
Nationwide, the high prevalence areas for ehrlichiosis are more wide-spread and less well-defined compared to other vector-borne pathogens. The maps represent multiples species of genus Ehrlichia that have different geographical ranges and vectors; however, all of them cause disease in dogs so the maps do represent disease risk for dogs. In general, the 2024 forecast is similar to 2023’s forecast which noted an expected increase in prevalence for the majority of the United States with some interesting emerging risk areas.
Importantly, Ehrlichiosis cases may vary from non-existent to endemic within a 200 miles range, leading to a strong need for local-level awareness and conversations with your veterinarian about your dog’s travel.
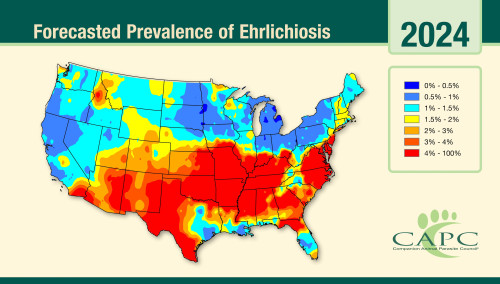
Overall, the 2024 trends in ehrlichiosis will be:
• The forecasted risks of Ehrlichia spp. in dogs remain high throughout the southeast, southwest, southcentral, and coastal Atlantic states.
• Compared to 2023, we expect increasing numbers of seropositive dogs in central California, northern Idaho, western Montana, western and central Washington, and parts of the Northeast (e.g., Vermont, New Hampshire, Connecticut). Risks also continue in much of Colorado and many parts of Wyoming. The relatively recent emergence of Ehrlichia muris eauclarensis in parts of Wisconsin and Minnesota emphasizes the need for testing and prevention in these areas.
• Considering the widespread prevalence of Ehrlichia spp. throughout much of the United States, the continued use of acaricides, routine examination of pets for the presence of ticks, and prompt removal remains imperative. Testing of symptomatic dogs can help monitor for ehrlichiosis and will also help reinforce the use of available tick control products.
What is Ehrlichiosis?
Ehrlichiosis is a disease caused by one or more different species of bacteria that infect white blood cells. Dogs get infected through the bite of several different species of infected ticks, such as the brown dog tick, the American dog tick or the lone star tick.
Infected dogs may show no signs at all, or there may be vague signs, such as fever, lethargy, loss of appetite, or nose bleeds. In some cases, chronic infection can lead to arthritis, immune cell abnormalities, and bone marrow suppression (which can be fatal). This is why early diagnosis and treatment are critical.
Humans and other pets in your household cannot catch Ehrlichiosis directly from an infected dog. However, infected dogs mean there may be infected ticks in the area that could transmit the bacteria to other household members.
Year-round tick control can help safeguard your dog
Within any geographic area, there may be several different kinds of ticks and each tick can potentially harbor more than one disease-causing agent. People generally consider the summer to be the only time that dogs and people are at risk of getting ticks; however, some species of ticks, for example brown dog ticks and black-legged ticks, can be active throughout the winter. In addition, brown dog ticks can live indoors, increasing risk of year-around exposure. Even though avoiding tall grass and wooded areas can help to minimize your dog’s exposure to ticks, there is still a risk of infection. That’s why CAPC recommends year-round tick control and regular screening tests for dogs.
There is no vaccine to prevent ehrlichiosis, so it is essential to use a tick control product that’s recommended by your veterinarian as being right for your dog. Even with tick control, it’s a good idea to carefully check your dog’s entire body and remove attached ticks as soon as possible. Always use tweezers or other tick-removal devices and wear gloves to prevent exposure to disease-causing agents.
Stay current on vector-borne disease activity in your area
To help you identify the risk for parasite infection in your geographic area, CAPC provides Parasite Prevalence Maps down to the county level. The maps report the number of dogs testing positive for infection in your area, as well as in other regions where you may travel with your pet.
Parasites that affect pets and people are dynamic and ever changing, and CAPC is your trusted resource for accurate, timely information. Sign up to receive local alerts on parasite testing results down to the county level today by visiting the CAPC Parasite Prevalence Maps and selecting "Get Updates".
Pet owners can also access 30-Day Parasite Forecast Maps at http://www.petdiseasealerts.org These maps, developed exclusively by CAPC, provide a local forecast for every county in the continental United States on a monthly basis.
Choose a Category:
Category: Parasite Forecasts
